Federal Communications Commission has released its communications market place report for the year 2024 indicating significant investment in 5G network.
Capex
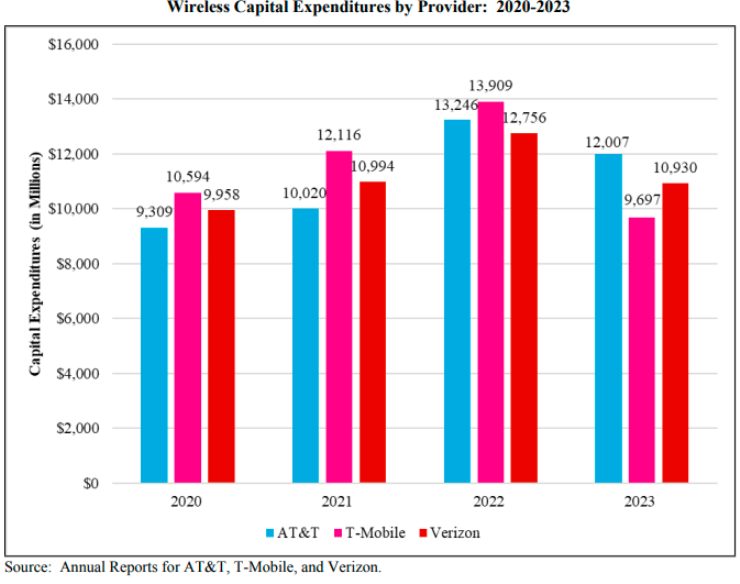
Over the past five years, mobile wireless service providers have invested nearly $163 billion in their networks, with $30.2 billion reported in 2023, a 22 percent decrease from $38.7 billion in 2022. The three largest providers — AT&T, T-Mobile, and Verizon — combined for an estimated $32.6 billion in 2023, reflecting a decline after steady increases from 2020 to 2022.
In 2023, these providers allocated 16.1 percent of their revenues to capital expenditures, with AT&T leading at 19 percent, followed by T-Mobile at 15.3 percent and Verizon at 14.2 percent. EchoStar has spent $2.6 billion annually in 2022 and 2023 to develop a facilities-based 5G network, contributing to the rapid deployment of wireless infrastructure, FCC said.
The major providers constructed their 5G networks 1.5 times faster than their 4G networks. EchoStar projects a $10 billion investment to create the first nationwide cloud-native 5G network, reporting broadband coverage to over 246 million people, or 73 percent of the U.S. population, by mid-2023.
5G coverage
Over the past two years, 5G coverage has significantly expanded, enabling high bandwidth and low latency for applications on a scale and with time sensitivity not achievable with 4G LTE. This growth has driven new streams of research and development in the wireless industry.
By mid-2024, AT&T reported 5G coverage for over 300 million U.S. consumers across 24,900 cities and towns, T-Mobile covered 330 million people over two million square miles, and Verizon aimed to cover 250 million consumers.
EchoStar, as of mid-2023, covered 70 percent of the U.S. population with 5G. According to FCC data, by December 2023, approximately 97 percent of the U.S. population was covered by at least one 5G provider at speeds of 7/1 Mbps or higher in outdoor stationary environments, with 93 percent covered at speeds of 35/3 Mbps or higher.
MIMO antenna
5G-NR has enabled the adoption of Massive MIMO antenna technology in higher frequency bands, significantly enhancing network capacity, coverage, and user experience. Massive MIMO antennas, with numerous active elements, use beamforming to direct signals to specific users, reducing interference and improving signal quality.
Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile, and EchoStar are actively deploying this technology. Wireless providers have also embraced carrier aggregation, which combines different spectrum channels to improve service quality by enhancing coverage, capacity, and speed. AT&T pioneered two-carrier aggregation for standalone 5G uplinks in 2023, while T-Mobile introduced four-carrier aggregation in mid-2023 and began deploying six-carrier aggregation in early 2024, aiming for speeds exceeding 3.6 Gbps.
Initial 5G deployments primarily used non-standalone architectures, combining 5G radios with an LTE core, allowing seamless switching between 5G and 4G LTE based on application needs and device compatibility. Standalone 5G, featuring a 5G core, has been introduced by T-Mobile, AT&T, and EchoStar in select areas. This architecture offers faster speeds, enhanced coverage through carrier aggregation, support for higher device density, lower latencies, real-time applications, improved security, and enables network slicing. Equipment vendor Spirent anticipates broader deployment of standalone 5G in 2024.
Open RAN
The largest Open RAN deployment in the U.S. is EchoStar’s 5G network, which covers 246 million people. Other deployments include Inland Cellular in Idaho and OptimERA in Alaska. In 2023, AT&T announced a $14 billion investment to move 70 percent of its wireless traffic to Open RAN, and in 2024, Verizon reported 130,000 radios supporting Open RAN specifications.
FWA
5G’s enhanced spectral efficiency, achieved through Massive MIMO and beamforming, has made it a viable technology for Fixed Wireless Access (FWA). FWA is more cost-effective and quicker to deploy than other fixed broadband services, and consumers can install antennas themselves. AT&T, Verizon, T-Mobile, and UScellular are offering FWA services using their 5G networks as they compete for fixed broadband customers.
While cable and wireline companies lost over 140,000 broadband subscribers in 2023, FWA saw more than 3.6 million net additions. Verizon and T-Mobile together gained over 6.7 million FWA customers in 2022 and 2023, with AT&T having over 200,000 FWA customers by April 2024.
Regional providers like Carolina West Wireless, Cellcom, Cellular One, and Union also use FWA in remote areas, and UScellular is exploring FWA with standalone 5G. In addition, IoT solutions such as Low-Power Wide-Area Networks, Narrowband IoT, and Long Range have emerged, and 5G’s high bandwidth, low latency, and ability to support many devices make it ideal for IoT. Companies like CISCO and TELUS are launching IoT services.
Baburajan Kizhakedath
