GSMA Intelligence has revealed 2025 research themes that will be shaping the industry in years to come.
Network transformation
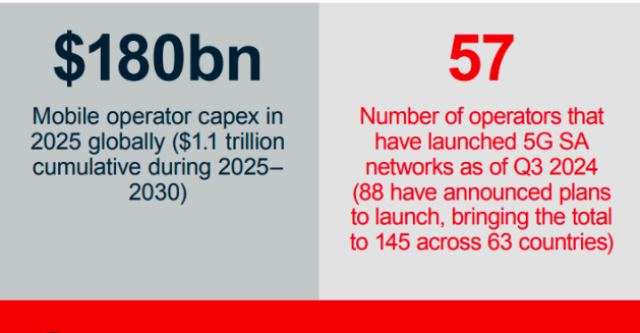
Mobile operator capex in 2025 globally will reach $180 billion. Mobile operator cumulative Capex during 2025–2030 will be $1.1 trillion.
57 operators have launched 5G SA networks as of Q3 2024 and 88 operators have announced plans to launch, bringing the total to 145 across 63 countries.
Operators, representing 74 percent of total mobile connections globally, have committed to the GSMA’s Open Gateway initiative.
There will be emphasis on 5G network rollout, energy-efficient networks, and the phasing out of 2G and 3G technologies.
There will be focus on the deployment of VoLTE (Voice over LTE) and VoNR (Voice over New Radio) to support advanced voice capabilities.
There will be progress in open RAN, network/cloud integration, and edge computing to enable flexible and efficient networks.
There will be focus on the adoption of generative AI (genAI) and broader AI applications to optimize operations.
There will be focus on growth of private networks and technologies like RedCap for specific industrial applications.
There will be investment in the expansion of 5G standalone (SA) networks among a growing number of operators.
There will be 5G-Advanced deployments highlighting enhanced capabilities and use cases.
In 6G, there will be early-stage development and strategic messaging for future networks.
There will be focus on the expansion of network APIs, driving innovation in services and use-case adoption.
There will be significant investments in fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) and other gigabit network solutions.
There will be launch of next-generation 5G FWA networks.
There will be integration of AI in network management and the phasing out of copper-based networks.
GenAI
74 percent of operators have either commercially deployed or are testing genAI solutions. 33 percent of enterprises are undertaking digital transformation that are already making advanced use of AI technology.
75 percent of consumers are aware of genAI (of these, 59 percent are users and among users, 67 percent are satisfied with their experience).
There will be significant progress in generative AI (genAI) and broader AI technologies impacting networks, platforms, services, and devices.
AI is being adopted in core networks and radio access networks (RAN), enhancing network performance, operational efficiency, and service personalization.
AI is also playing a role in customer service, helping to personalize experiences, optimize operations, and streamline customer care processes.
Operators are focusing on AI adoption, with varying levels of readiness and maturity. Challenges include finding the right strategies and managing the complexities of AI integration.
Key innovations are happening in AI-driven devices and digital services, with significant progress in areas like customer experience enhancement.
Companies are exploring different approaches to monetize AI technologies, with the goal of generating tangible business value from AI capabilities.
Enterprises are increasingly investing in AI as part of their digital transformation efforts, with strong interest in AI applications across various sectors.
Significant AI spending is taking place in vertical sectors like healthcare, retail, and manufacturing, with leading countries driving the majority of investment.
Digital Industries
Enterprises expects to spend 10 percent of revenue on digital transformation during 2024–2030. $400 billion will be the addressable market for operators in B2B technologies and services beyond connectivity.
The Number of IoT connections (cellular and beyond) globally will be 26 billion by the end of 2025 (46 percent/54 percent split between consumer and enterprise IoT).
Enterprises are increasingly relying on advanced technologies, including cloud, AI, and IoT, to meet transformation goals. However, deployment challenges remain as companies evaluate which technologies will drive the most value.
Operators are refining their value propositions to attract enterprise customers, with an emphasis on innovative connectivity solutions and value-added services.
Operators are exploring diverse monetisation routes, from network-as-a-service models to offering AI-driven solutions and digital platforms for enterprises.
Operators are aligning their strategies to tap into the growing IoT market, focusing on delivering scalable and secure IoT solutions for enterprises.
Consumer 5G
The number of 5G mobile connections globally will reach 2.6 billion by the end of 2025 (29 percent of total mobile connections).
82 percent of Average share of 5G users who claim 5G has met or exceeded their expectations. 5 percent of consumers who intend to upgrade to 5G are willing to pay 5 percent extra versus what they pay for their current 4G subscription.
The number of 5G mobile connections is steadily increasing worldwide, with several markets already surpassing 50 percent penetration.
Specific regions and markets are leading the next wave of 5G network deployments, driven by factors like infrastructure investment, demand for faster data speeds, and policy support.
There are notable changes in user satisfaction and dissatisfaction with 5G networks, impacting customer retention and acquisition.
Many users are willing to pay a premium for 5G subscriptions, with increasing interest in 5G-specific use cases and bundled services.
5G users are engaging more with digital entertainment, such as mobile gaming and streaming, indicating a growing demand for high-speed, low-latency services.
Operators are shifting towards speed-based tariffs and experience-based differentiated services to better align with 5G capabilities.
The adoption of 5G is driving an increase in mobile data traffic and average revenue per user (ARPU), particularly in markets that are leading in 5G deployment.
Markets with the highest ARPU growth are focused on new services, content offerings, and innovative tariff models.
There are significant innovations and price reductions in 5G devices, including smartphones, 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) equipment, and other consumer devices, making 5G more accessible to a wider audience.
Key services benefiting from 5G include mobile and cloud gaming, video streaming, in-venue entertainment, XR (extended reality), and new communication features like 5G calling. The growth of the metaverse and immersive experiences (AR/VR) is also fueled by 5G’s capabilities.
Fixed broadband and 5G FWA
FTTP/B share of total fixed broadband connections will reach 76 percent in 2025. The number of operators that have launched 5G FWA networks has reached 139 across 68 countries as of September 2024.
The number of countries that will have a 5G FWA share of total fixed broadband connections greater than 15 percent by 2030 will be seven.
Consumers are shifting towards newer access technologies like fiber, which is expected to lead future growth in broadband adoption.
Operators are innovating their commercial practices to align with customer demands for higher speeds, reliability, and value-added services.
Traditional quad-play bundles (mobile, fixed, TV, and internet) are being impacted by shifting consumer preferences, leading to new types of bundled services.
Operators are introducing new multiplay strategies, which combine various services to meet diverse consumer needs.
5G FWA networks are progressing in multiple areas, including network and service launches, spectrum use, and innovations in Customer Premises Equipment (CPE).
The main drivers of customer adoption for 5G FWA include demand for high-speed internet in rural and underserved areas, as well as cost-effective solutions.
There is growing consumer interest in 5G FWA services, driven by the promise of faster speeds and better coverage compared to traditional broadband.
Operators are tailoring their commercial practices to attract FWA customers, including pricing strategies, service bundles, and infrastructure investments.
Enterprises are increasingly looking at 5G FWA as a viable option for high-speed, flexible broadband solutions.
Operators are focusing on enterprise solutions for 5G FWA, with tailored strategies to grow adoption among business customers, including offering scalable and secure connectivity.
Consumer technology
78 percent of smartphone users intend to replace their smartphone with the same brand. 60 percent of consumers are playing digital games at least once per week. The number of pay-TV markets that will see a decline in traditional payTV connections between 2024 and 2030 will be 21 due to cordcutting impact.
New technologies such as AI, foldables, extended reality (XR), eSIM, and satellite connectivity are driving innovation in mobile devices.
There is continued growth in wearables and smart home devices, reflecting broader consumer interest in connected tech.
Smartphone sales have started recovering, impacting mobile players’ strategies.
Digital entertainment is rapidly evolving, with significant innovation in gaming, pay TV, fintech, and other digital services.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards on-demand services, with a strong focus on content availability, personalization, and the integration of AI technologies.
Operators are seeking new ways to monetise innovations in devices and digital services, moving beyond traditional connectivity revenue.
The rise of digital-first brands and digital-only propositions is pushing operators to rethink their retail strategies, offering more online-based services.
eSIM
440 mobile service providers are offering commercial eSIM service for smartphones as of June 2024. There will be 70 percent increase in the number of eSIM smartphone connections globally in 2025. 42 percent will be the eSIM share of total IoT cellular connections by 2030 (average across 21 countries).
The GSMA report provides insights into the commercialisation, adoption, and impact of eSIM technology across the consumer and IoT enterprise markets. Key findings include:
eSIM devices and connectivity services are advancing, with operators and OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) adapting their strategies to support eSIM functionality.
The outlook for eSIM-only smartphones is growing, particularly as more devices support eSIM technology.
eSIM is reshaping mobile market dynamics, including how mobile plans are structured and how services are delivered.
eSIM is playing a role in 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA), enabling more flexible, scalable connectivity solutions.
eSIM is contributing to the growth of the IoT market by providing greater flexibility, security, and cost savings for connected devices.
Despite its benefits, there are challenges in eSIM adoption, including interoperability, complexity in deployment, and the need for standardized solutions across regions and device types.
Satellites and NTNs
91 operators have partnered with satellite players to offer satellite connectivity in their services.
The number of IoT devices that are addressable from satellite-enabled connectivity will be 2 billion, representing 10 percent of the IoT base by 2035.
By the end of 2035, satellite-backed connectivity is estimated to generate more than $30 billion per year for operators.
The satellite and NTN sectors are experiencing significant growth, driven by advancements in technology, regulatory support, and increased commercial interest.
Spectrum
The number of countries globally where spectrum bands that can be used for 5G services have been assigned as of September 2024 has reached 100.
The number of countries globally where mmWave spectrum bands have been assigned as of September 2024 has reached 23.
The number of 2G and 3G networks that will be shut down during 2025–2030 based on operators’ announced plans is 42 and 58, respectively.
New trends are emerging in spectrum assignment, such as the exchange of spectrum for coverage, connectivity, and infrastructure development.
The report highlights new spectrum models, including local licensing and dynamic spectrum sharing, which are designed to address evolving needs and improve spectrum efficiency.
Energy efficiency
70 percent is the share of operators that see sustainability as a ‘very’ or ‘extremely’ important network transformation priority.
1 percent of global energy use attributed to operator networks (fixed and mobile).
Operators accounting for 50 percent of global market share have committed to net zero.
There have been significant improvements in the energy efficiency of telecom networks, both mobile and fixed, as well as in computing and data centers. The report also examines the energy implications of migrating 4G and 5G workloads to the cloud and edge computing environments, which can have both positive and negative impacts on overall energy consumption.
Telecom and digital technologies are playing a critical role in helping vertical industries decarbonize. These technologies enable more energy-efficient operations and help reduce emissions across industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and transportation.
The telecom industry is making progress toward achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. Key drivers include the adoption of energy-efficient technologies and the integration of renewable energy sources. However, barriers such as technological limitations, high upfront investment costs, and regulatory challenges remain. Overcoming these obstacles will be essential for the industry to meet its sustainability goals.
Baburajan Kizhakedath
