The global foundry industry exhibited a polarized growth trend in the fourth quarter of 2024, driven by strong demand for advanced process nodes while mature process nodes saw a relative slowdown.
The demand for AI servers, flagship smartphone application processors (APs), and next-generation PC platforms significantly boosted high-value wafer shipments, TrendForce said in its report.
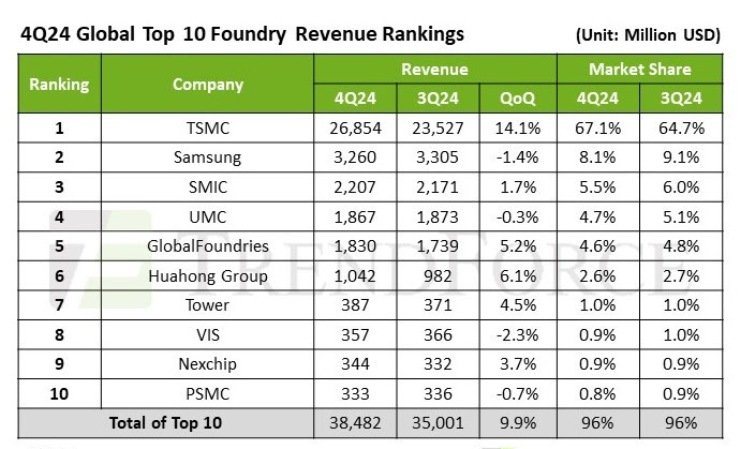
As a result, the top 10 foundries collectively recorded nearly 10 percent quarter-over-quarter (QoQ) revenue growth, reaching an industry record of $38.48 billion. This upward trend highlights the increasing reliance on semiconductor manufacturing as industries continue to shift towards AI-driven and high-performance computing applications.
A key factor shaping the foundry industry in this period was the impact of new U.S. trade tariffs under the Trump administration. These tariffs led to a surge in demand for TVs, PCs, and notebooks bound for the U.S., extending into the first quarter of 2025.
At the same time, China’s consumer subsidy program, introduced in late 2024, encouraged early inventory restocking among upstream customers. These factors, along with TSMC’s continued strength in AI chip manufacturing and advanced packaging, suggest that the usual seasonal downturn in the first quarter of the year will be milder than expected, with only a slight decline in revenue.
Top players and share
TSMC remained the undisputed leader, achieving a significant 14.1 percent quarter-over-quarter (QoQ) revenue increase to $26.85 billion. The company’s market share rose from 64.7 percent in Q3 to 67.1 percent in Q4, driven by high demand for AI chips, flagship smartphone processors, and advanced PC components. Its ability to capitalize on cutting-edge technologies and maintain a strong position in AI-related semiconductor production solidified its dominance.
Samsung Foundry, the second-largest player, faced a slight revenue decline of 1.4 percent QoQ, generating $3.26 billion in Q4. Its market share dropped from 9.1 percent in the previous quarter to 8.1 percent. This decline was primarily due to the loss of orders from key clients, which new advanced-node customer acquisitions could not fully offset. Despite its efforts to expand in the high-performance computing and AI sectors, the company struggled to maintain growth momentum.
SMIC secured third place with a 1.7 percent QoQ revenue increase, reaching $2.21 billion. Its market share declined slightly from 6.0 percent in Q3 to 5.5 percent in Q4, as customer inventory adjustments impacted wafer shipments. However, the ramp-up of new 12-inch production capacity and an optimized product mix helped counterbalance the decline in shipments, allowing for modest growth. The company’s strategic focus on improving blended average selling prices (ASPs) played a key role in sustaining revenue.
UMC recorded a marginal 0.3 percent QoQ decline in revenue, generating $1.87 billion. Its market share dropped slightly from 5.1 percent to 4.7 percent. Despite weaker ASPs, UMC benefited from customers front-loading orders, which helped maintain higher-than-expected capacity utilization rates. While the decline was minimal, it highlighted the challenges faced by mature process nodes in a market increasingly focused on advanced semiconductor technologies.
GlobalFoundries saw a 5.2 percent QoQ revenue increase, reaching $1.83 billion, securing its fifth-place ranking. The company experienced strong wafer shipments, though slight declines in ASPs tempered overall growth. Nevertheless, its market share remained stable at 4.6 percent. The company continued to strengthen its position in specialized process technologies catering to automotive, industrial, and AI-related applications.
HuaHong Group ranked sixth, achieving the highest growth among the mid-tier foundries with a 6.1 percent QoQ increase, reaching $1.04 billion in revenue. Its market share increased from 2.7 percent to 2.9 percent. This growth was primarily driven by improvements in capacity utilization at HHGrace’s 12-inch fabs and inventory replenishment supported by China’s home appliance subsidy program. The company capitalized on local policy incentives to drive demand.
Tower Semiconductor secured seventh place with a 4.5 percent QoQ revenue increase to $387 million. It managed to offset weaker fab utilization rates by enhancing ASPs, helping sustain revenue growth. The company maintained its market share at 1.0 percent, continuing to serve niche markets such as analog and radio-frequency semiconductors.
VIS faced a 2.3 percent QoQ revenue decline, falling to $357 million. Its market share remained at 0.9 percent. Weak consumer demand impacted wafer shipments, though ASP improvements helped mitigate the revenue drop. The company’s reliance on mature process nodes contributed to the decline as the industry shifted towards advanced technologies.
Nexchip was the only company among the top 10 to change rankings, moving up to ninth place with a 3.7 percent QoQ revenue increase to $344 million. While facing weaker demand for panel-related display driver ICs (DDIs), its growth was supported by stable shipments of CMOS image sensors (CIS) and power management ICs (PMICs). Nexchip’s market share held steady at 0.9 percent.
PSMC fell to tenth place, experiencing a 0.7 percent QoQ revenue decline to $333 million. Weak memory foundry and consumer-related chip demand contributed to its decline. However, on a full-year basis, PSMC’s total revenue remained slightly higher than Nexchip’s. Its market share remained stable at 0.9 percent, reflecting the broader struggles of companies dependent on mature-node semiconductor manufacturing.
Baburajan Kizhakedath
