Worldwide 5G network infrastructure market revenue will almost double in 2020 to $8.1 billion, according to Gartner.
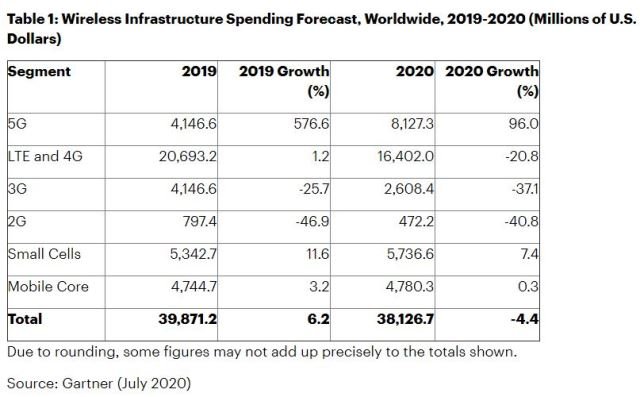
Total wireless infrastructure revenue is forecast to decrease 4.4 percent to $38.1 billion in 2020.
Telecom operators’ investment in 4G network infrastructure will drop 20.8 percent to $16.4 billion in 2020.
Telecom operators’ investment in 3G network infrastructure will decrease 37 percent to $2.68 billion.
Telecom operators’ investment in 2G network infrastructure will decrease 40.8 percent to $472 million.
Telecom operators’ investment in small cells will grow 7.4 percent to $5.73 billion in 2020.
Telecom operators’ investment in mobile core increase 0.3 percent to $4.78 billion in 2020.
Telecom operators’ investment in 5G network infrastructure accounted for 10.4 percent of total wireless infrastructure revenue in 2019.
Telecom operators’ investment in 5G network infrastructure will account for 21.3 percent of total wireless infrastructure revenue in 2020, Gartner said.
Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE and Samsung are the leading 5G network suppliers in the world.
There are now over 63.6 million 5G connections globally as of Q1 2020, according to data from Omdia.
Globally, there are now 82 5G commercial networks, a number which is expected to more than double to 206 by the end of 2020, according to data from TeleGeography.
There are over 100 commercial 5G device models available, according to Ericsson Mobility June 2020 Report with increasing support for low-band, mid-band and millimeter (mmWave) frequency bands.
A growing number of SPs are prioritizing 5G projects by reusing current assets including radio spectrum bandwidths, base stations, core network and transport network, and transitioning LTE/4G spend to maintenance mode, said Kosei Takiishi, senior research director at Gartner.
New O-RAN (open radio access network) and vRAN (virtualized RAN) ecosystem could disrupt current vendor-lock-in and promote 5G adoption by providing cost-efficient and agile 5G products in the future.
Gartner predicts that SPs in Greater China (China, Taiwan and Hong Kong), mature Asia Pacific, North America and Japan will reach 5G coverage across 95 percent of national populations by 2023.
Despite investment growth rates in 5G being slightly lower in 2020 due to the COVID-19 crisis (excluding Greater China and Japan), CSPs in all regions are quickly pivoting new and discretionary spend to build out the 5G network and 5G as a platform.
Greater China leads the world in 5G development, with 49.4 percent of worldwide investment in 2020 attributed to the region. Cost effective infrastructure manufactured in China coupled with state sponsorship and reduced regulatory barriers is paving the way for major CSPs in China to quickly build 5G coverage.
Gartner expects that 5G investment will rebound modestly in 2021 as CSPs seek to capitalize on changed behaviors sparked by populations’ elevated reliance on communication networks. 5G investment will exceed LTE/4G in 2022.
SPs will gradually add stand-alone (SA) capabilities to their non-stand-alone (NSA) 5G networks.
Gartner predicts 15 percent of CSPs worldwide will operate stand-alone 5G networks that do not rely on 4G network infrastructure by 2023. This will divert wireless investment away from LTE/4G and spending on legacy RAN infrastructure will decline.
