The global satellite Internet of Things (IoT) communications market is experiencing robust growth, according to a new research report by IoT analyst firm Berg Insight.
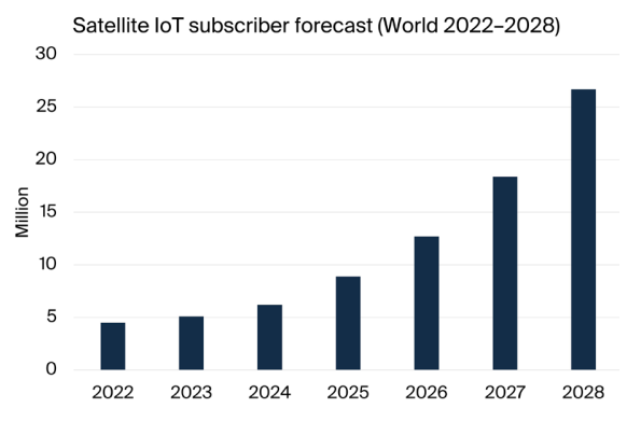
As of 2023, the global satellite IoT subscriber base surpassed 5.1 million, and it is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 39.2 percent, reaching 26.7 million units by 2028.
Satellite IoT connectivity revenues are forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 34.8 percent from €302.9 million in 2023 to approximately €1.35 billion in 2028.
ARPU of satellite IoT connectivity service is expected to drop to €4.20 by 2028.
Satellite IoT is emerging as a crucial solution in regions where terrestrial connectivity services cover only about 10 percent of the Earth’s surface. Satellite networks provide essential communication in remote locations, benefiting industries such as agriculture, asset tracking, maritime transportation, oil and gas exploration, utilities, and construction.
Key players in the satellite IoT market include Iridium, Orbcomm, Viasat (Inmarsat), and Globalstar.
Iridium leads the market with 1.8 million satellite IoT subscribers.
Orbcomm has 715,000 subscribers. Orbcomm has expanded from satellite operations to offer end-to-end IoT solutions.
Inmarsat does not currently report IoT subscribers.
Globalstar has 0.48 million satellite IoT subscribers.
Emerging operators like Myriota (Australia) and Kineis (France) are gaining traction.
The satellite IoT market is seeing new entrants. Astrocast, AST SpaceMobile, and Swarm Technologies (SpaceX) are leveraging low-earth orbit nano-satellite technologies.
Several companies are adopting hybrid models, integrating satellite and terrestrial connectivity technologies like 4G/5G and LoRaWAN.
In addition to the incumbent satellite operators a number of new initiatives have appeared on the market recently.
Examples of some high-profile projects are Astrocast, AST SpaceMobile, CASC/CASIC, E-Space, Hubble Network, Kepler Communications, Kineis, Ligado Networks, Lynk,
Myriota, Omnispace, Skylo, Swarm Technologies (SpaceX) and Totum.
Many of these are based on low-earth orbit nano satellite concepts. While some rely on proprietary satellite connectivity technologies to support IoT devices, several are starting to leverage terrestrial wireless IoT connectivity technologies.
Examples include OQ Technology, AST SpaceMobile, Omnispace, Sateliot, Galaxy Space, Ligado Networks, Lynk, Skylo and Starlink (3GPP 4G/5G); EchoStar Mobile, Fossa Systems, Lacuna Space, Innova Space and Eutelsat (LoRaWAN); and Hubble Network (Bluetooth).
As collaboration between satellite and mobile operators grows, more hybrid satellite-terrestrial services are expected, creating new opportunities for IoT connectivity across various industries. Skylo is a leader in this space, partnering with major telecom operators like Deutsche Telekom and Telefonica, while others such as Sateliot, Starlink, and Omnispace are also establishing strategic partnerships.
