The latest Opensignal report has revealed mobile network speeds and user experience in top cities across the Asia Pacific (APAC) region.
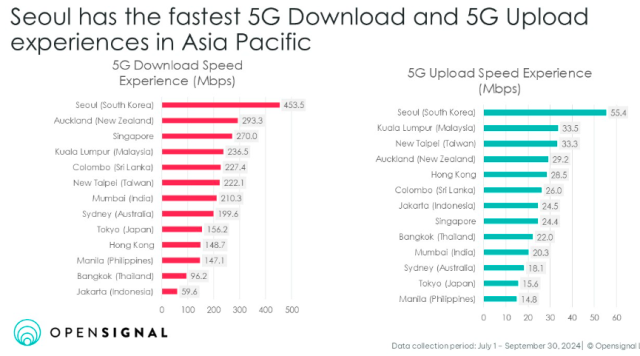
Seoul leads APAC with download speeds of 168.1 Mbps and upload speeds of 25.3 Mbps. This is due to South Korea’s early 5G adoption, where over 50 percent of mobile connections use 5G. This widespread 5G use has eased congestion on 4G networks, benefiting users with improved speeds on both networks. Seoul’s 5G network rollout even extends to public Wi-Fi on buses.
Seoul continues to top the 5G speed rankings in APAC, as it did in 2022. Auckland ranks second for 5G download speeds at 293.3 Mbps, with high upload speeds as well, the report said.
Jakarta (Indonesia) lags in 5G download speeds due to limited access to the 3.5GHz spectrum, with operators relying on Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (2100MHz and 2300MHz bands). However, improvements are expected next year as Indonesia plans to auction new spectrum bands (700MHz, 2.6GHz, and 26GHz) for 5G.
Both Mumbai (India) and Colombo (Sri Lanka) see significant speed jumps from 4G to 5G, with Mumbai showing greater increases. However, 5G adoption remains low in Colombo, where less than 2 percent of users have 5G-capable devices. Leading mobile operators in Mumbai are Bharti Airtel, Reliance Jio and Vodafone Idea.
Seoul also leads in mobile experience metrics across video, gaming, and voice applications, being the only APAC city rated Excellent (85+) for Games Experience, minimizing lag for users. In cities with established 5G networks, performance for video, gaming, and voice apps has improved, with Seoul, New Taipei, and Hong Kong among the top cities in 5G Games and Video Experience scores.
Seoul leads with the highest Reliability Experience score (925/1000), closely followed by Tokyo and New Taipei, all above 900 points. In contrast, cities like Dhaka (Bangladesh), Karachi (Pakistan), and Yangon show lower scores, reflecting poor national performance in mobile connectivity.
Seoul ranks first, with New Taipei in second place, for Consistent Quality in mobile networks. Yangon and Karachi rank towards the bottom due to Myanmar’s infrastructure damage and Karachi’s frequent power outages, which impact communication tools like WhatsApp.
Eight APAC cities maintain 3G or better connectivity over 99 percent of the time. 5G Availability varies significantly. Mumbai, Seoul, and Kuala Lumpur show high 5G availability, with users connected over 40 percent of the time. By contrast, cities like Tokyo, Manila, and Jakarta have less than 20 percent 5G availability.
India stands out with significant 5G progress, with Jio deploying standalone 5G, particularly in urban areas. Other APAC markets have yet to roll out 5G standalone networks at a large scale, often relying on 4G or non-standalone 5G.
Indonesia faces challenges in 5G deployment, mainly due to limited access to key 5G spectrum bands like 3.5GHz and the logistical hurdles of network expansion across its archipelago, which requires substantial infrastructure investment.
Baburajan Kizhakedath
