The global installed base of active smartphones increased 2 percent in 2025, driven by longer replacement cycles approaching four years and a rising share of second-life devices, according to Counterpoint Research’s Smartphone Installed Base Tracker. The active installed base is a critical indicator of long-term competitive strength in mature markets because it reflects device longevity, user retention and ecosystem loyalty rather than short-term shipment volumes.
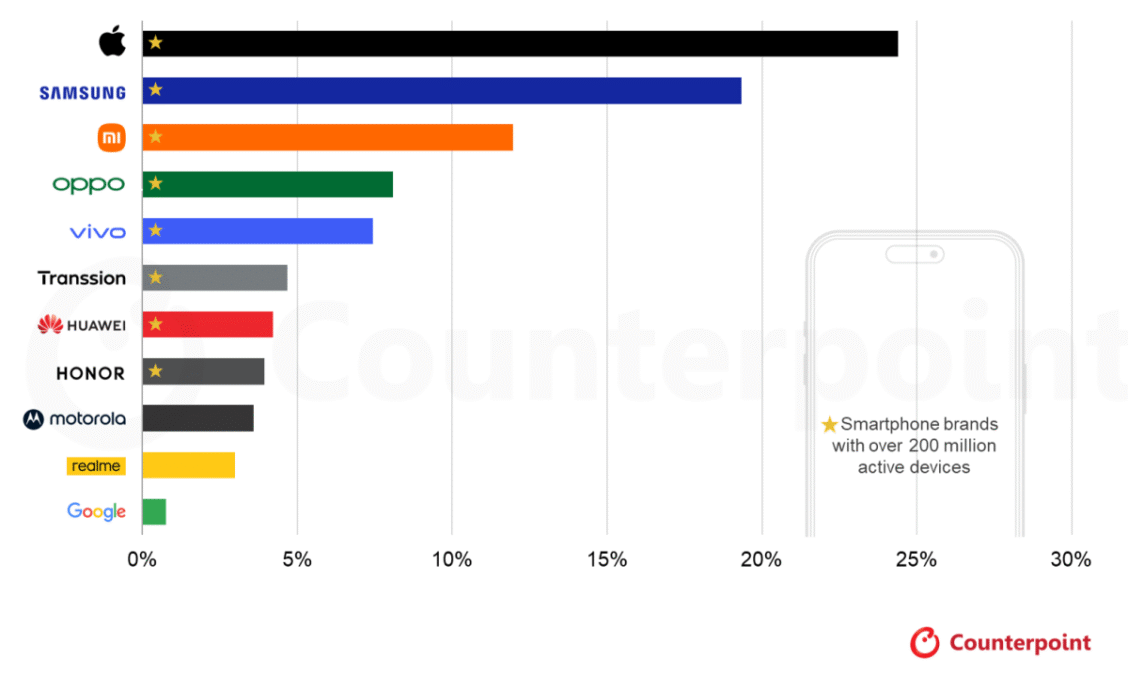
Eight Smartphone Brands Surpass 200 Million Active Devices
Counterpoint Research noted that each of the eight leading smartphone OEMs had an active installed base exceeding 200 million devices in 2025, collectively accounting for more than 80 percent of the global active installed base. Apple and Samsung are the only brands to surpass the one-billion active devices milestone, highlighting their ability to retain users over time.
The 200 million-plus installed base club is now divided into three distinct segments:
1 billion-plus club
- Apple
- Samsung
These two companies achieved scale through premium positioning and strong ecosystems that encourage long-term engagement and repeat purchases.
Mid and mid-to-high segment leaders
- Xiaomi
- OPPO (including OnePlus)
- vivo
These brands built large installed bases by targeting competitive midrange and upper-midrange segments while gradually strengthening their ecosystems.
Affordable market specialist
- Transsion Group (TECNO, itel, Infinix)
Transsion’s growth has been fueled by affordable devices tailored for price-sensitive markets in the Middle East and Africa and Southeast Asia. HONOR has recently entered the 200 million-plus club, while Motorola and realme are approaching the milestone.
Apple Leads Global Active Smartphone Installed Base
Apple holds the top position globally, with roughly one in four active smartphones being an iPhone. In 2025, Apple added more net new active devices than the next seven leading OEMs combined, underlining strong user loyalty and the strength of its iOS ecosystem.
Samsung ranks second with about one-fifth of the global installed base. Its broad product portfolio across entry-level, midrange and premium segments, along with wide geographic reach, supports its long-term growth.
Together, Apple and Samsung accounted for 44 percent of the global active installed base in 2025. Their leadership is reinforced by longer replacement cycles, durable premium devices, extended software support, strong resale values and deeply integrated ecosystems that encourage multi-owner usage and long device lifespans.
Premium Smartphones Drive Long-Term User Retention
Counterpoint Research highlighted that smartphone OEMs must prioritize long-term user retention rather than shipment volumes to expand their installed base. Premium smartphones play a critical role because users hold these devices longer and are more likely to remain within the same ecosystem.
Brands can strengthen retention by delivering:
- Durable builds and longer battery life
- Advanced displays and high-end cameras
- Extended software support
- Seamless cross-device integration
However, the premium segment remains difficult to penetrate. In 2025, six OEMs outside Apple and Samsung held only a single-digit share of smartphone sales priced above $600 wholesale. Memory shortages and rising component costs are also limiting the availability of higher-specification models, which may delay upgrades and further extend replacement cycles.
AI and Software Become Key Differentiators
As the smartphone market matures, differentiation is shifting from hardware to software and ecosystem capabilities. On-device AI, camera intelligence, productivity tools and seamless connectivity across devices are emerging as major drivers of user loyalty and engagement.
A growing installed base strengthens software revenue potential by turning each smartphone into a long-term monetization platform. Apple continues to lead in this area, generating high-margin services revenue that is growing at double-digit rates.
Longer software support and stronger ecosystem lock-in are increasing user lifetime value. With hardware growth slowing and costs rising, software and services are becoming a stable recurring revenue stream that is less dependent on replacement cycles.
BABURAJAN KIZHAKEDATH
