India’s government has handed a major policy win to Apple after months of lobbying by the iPhone maker, announcing tax rule changes that remove a key risk tied to supplying high-end manufacturing equipment to contract manufacturers, Reuters news report said.

As part of Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman’s Union Budget 2026-27, India said foreign companies will be allowed to provide machines to their Indian contract manufacturers in specified areas for five years without triggering income tax liabilities. The move is aimed at promoting electronics manufacturing and is expected to accelerate investment by global players, led by Apple.
Apple Pushes for Clarity on Tax Exposure
Apple has been expanding rapidly in India as it diversifies its manufacturing base beyond China.
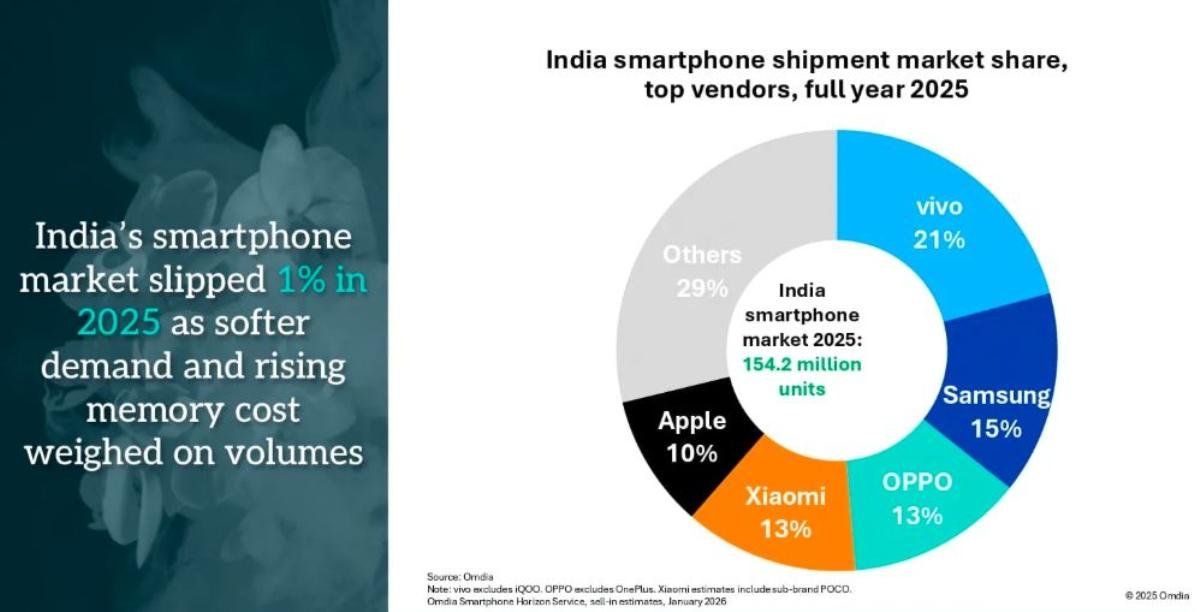
The latest report from Omdia indicated that Apple has shipped 3.9 million iPhones in India during Q4-2025. Apple is the fifth largest smartphone maker in India with 11 percent share in Q4. The smartphone share of Apple was 10 percent in 2025 by shipping 15.1 million iPhones vs 8 percent and 11.8 million iPhones in 2024.
According to Counterpoint Research, Apple’s iPhone market share in India has doubled to 8 percent since 2022. While China still accounts for about 75 percent of global iPhone shipments, India’s share has quadrupled to 25 percent over the same period.
However, Apple had raised concerns with Indian authorities over income tax laws that could treat ownership of manufacturing machinery as a “business connection” in India. Unlike in China, this interpretation could have exposed Apple to taxes on its iPhone sales profits if it directly paid for and owned machines used by its contract manufacturers.
This risk had forced Apple’s partners, including Foxconn and Tata, to spend billions of dollars themselves on expensive production equipment.
To address this, India announced changes to ensure that “mere ownership of machines by a foreign company does not lead to taxes on it,” provided the equipment is used by an Indian contract manufacturer.
Five-Year Exemption to Drive Investment
The policy change, unveiled in the Budget documents, states that any income arising from providing capital goods, equipment, or tooling to an Indian contract manufacturer will be eligible for exemption. The exemption will apply for five years, offering companies greater certainty over their tax exposure.
“We are saying that if you bring your machine, and that machine is used by a local manufacturer to produce something, we will exempt you for five years. We are giving them certainty,” Revenue Secretary Arvind Shrivastava said at a post-budget press conference.
The rule change will be valid until the 2030-31 tax year and will apply only to factories located in customs-bonded areas. These zones are technically considered outside India’s customs border, making them primarily suitable for export-focused manufacturing. Devices sold into the Indian market from such facilities would still attract import duties.
Faster Scale-Up for Electronics Manufacturing
Smartphone and electronics manufacturing is a central pillar of Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s economic growth strategy. By removing tax uncertainty, the government hopes to encourage Apple and other global electronics companies to fund the initial cost of advanced machinery, easing the financial burden on Indian contract manufacturers.
“This exemption removes a key deal-breaking risk for electronics manufacturing in India,” said Shankey Agrawal, Partner at tax-focused law firm BMR Legal. “The result is faster scale-up and greater confidence for global electronics players to manufacture in India.”
Reuters news earlier indicated that Apple held discussions with officials in recent months, warning that the earlier legislation could hinder its future expansion plans in the country.
Competitive Impact on Global Players
The earlier tax rules did not affect Apple’s South Korean rival Samsung, as most of its smartphones are produced in its own Indian factories rather than through contract manufacturers. The new policy, however, levels the playing field for companies that rely on contract manufacturing models.
Apple did not immediately respond to requests for comment, but the Budget announcement is widely seen as a clear signal that India is willing to adapt its tax framework to attract large-scale electronics manufacturing and deepen its role in global supply chains.
With greater tax certainty now in place, Apple and its partners are expected to ramp up investments, strengthening India’s position as a key export hub for iPhones and other high-value electronics.
BABURAJAN KIZHAKEDATH
