The 5G revolution is sweeping across Asia Pacific, fueled by a combination of factors including robust network expansion, declining prices of 5G devices, and strategic marketing efforts by operators. The adoption of 5G in Asia Pacific is poised to surge nearly six-fold, reaching an impressive 41 percent by the year 2030, according to a report from GSMA.
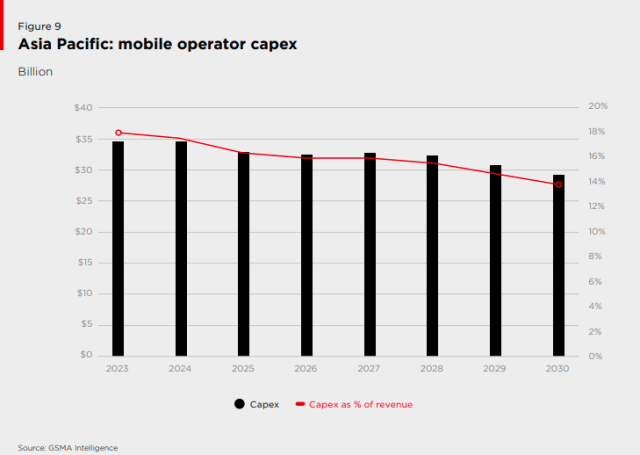 Telecom operators are poised to allocate a staggering $259 billion towards enhancing their networks between the years 2023 and 2030. This colossal investment is expected to be predominantly funneled into the expansion of 5G networks, signaling a decisive shift in the technology landscape.
Telecom operators are poised to allocate a staggering $259 billion towards enhancing their networks between the years 2023 and 2030. This colossal investment is expected to be predominantly funneled into the expansion of 5G networks, signaling a decisive shift in the technology landscape.
Having witnessed a flurry of 5G infrastructure development in pioneering markets over recent years, a record-breaking surge in capital expenditure (Capex) was observed. However, experts anticipate that these markets will soon witness a moderation in Capex levels, with attention shifting towards reaping returns on their substantial financial commitments. Operators are eagerly focusing on the monetization of 5G networks, in a bid to translate significant capital outlays into profitable ventures.
It is noteworthy that despite the escalating momentum of 5G rollout across various frontiers, the rate of expansion is unlikely to counterbalance the overall Capex decline. This is primarily attributed to the enduring relevance of earlier network generations such as 3G and 4G, which are expected to retain their significance in the connectivity landscape for the foreseeable future.
As of March 2023, an impressive count of 29 mobile operators spanning 15 markets across the Asia Pacific region have already embarked on the commercial launch of 5G mobile services. This concerted effort underscores a paradigm shift towards the monetization of 5G technologies, encompassing both consumer-oriented and enterprise-centric segments. With a goal of realizing substantial returns on their substantial investments, operators are steadfastly redirecting their strategies towards this goal.
 Among the trailblazing operators in the Asia Pacific region, several stand out due to their innovative approaches:
Among the trailblazing operators in the Asia Pacific region, several stand out due to their innovative approaches:
NTT Docomo: The company has established a groundbreaking subsidiary, Qonoq, which is dedicated to the development of cutting-edge XR (Extended Reality) hardware and software products.
Jio Tesseract: A subsidiary of Jio, the company is poised to make its mark by crafting its own hardware catering to the realm of Extended Reality.
LG Uplus: Notably, LG Uplus has amassed an impressive collection of over 3,500 high-quality 3D VR content items. These offerings span a diverse range, including movies, sports events, and even comics, enriching the immersive experience for consumers.
Moreover, the surge in 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) services has been a significant development, with 17 operators from eight countries in the Asia Pacific region having introduced this innovative solution as of March 2023. The growth of 5G FWA is anticipated to be particularly pronounced in markets where fixed broadband technology is skewed towards xDSL, such as Australia, or in areas with relatively low total fixed broadband penetration like the Philippines.
An illustrative example of this trend can be found in the Philippines, where Globe Philippines revealed that FWA was responsible for a quarter of its home broadband revenues as of May 2023. The technology is being adopted both in rural regions and as an alternative in urban areas where fiber broadband is yet to be established. This trend extends beyond the Philippines, permeating through other corners of Southeast Asia, including Indonesia and Thailand, thereby unlocking new revenue streams for enterprising operators.
With these monumental investments, groundbreaking developments in XR technology, and the proliferation of 5G FWA services, the telecom industry in the Asia Pacific region is poised to reshape the connectivity landscape and usher in an era of unparalleled possibilities.
While 5G is witnessing significant growth in mature markets, it’s projected that 4G will remain the dominant technology on a regional scale well into the foreseeable future. Despite this, legacy networks like 2G and 3G are progressively being phased out, with several countries, including Australia, Japan, and the Philippines, announcing plans to retire these networks in the coming years.
By the close of 2023, 5G adoption will have reached the mass market in prominent countries such as Australia (42 percent), Japan (47 percent), and South Korea (53 percent), aligning them with global counterparts like China (45 percent), Germany (35 percent), and the US (59 percent). The second wave of 5G is currently in motion, largely propelled by the deployment of 5G networks in major emerging markets, including India. Although first-wave markets will maintain a higher share of mobile connections by 2030, the second-wave markets are expected to contribute a significant number of new 5G connections, propelling the global total to 5 billion by 2030.
There will be more than 280 million cellular IoT connections in Asia Pacific by 2030. India, Japan and South Korea will account for nearly three quarters of these connections. There will be a boost to IoT applications as 5G networks expand across the region because 5G enables new IoT use cases based on its low-latency and high-capacity capabilities.
Asia Pacific’s mobile penetration rate is forecasted to reach 70 percent by 2030, slightly below the global average of 73 percent for the same year. The penetration rate is particularly elevated in Northeast Asia and Oceania, reaching 82 percent and 79 percent, respectively.
Over the next seven years, an estimated 400 million new subscribers are anticipated to join the ranks. South Asia will account for approximately two-thirds of total mobile subscribers in Asia Pacific, constituting the bulk of new subscriptions until 2030.
A notable development is the shrinking mobile internet usage gap in the region, reducing from 60 percent in 2017 to 47 percent in 2022. This shift reflects the increasing affordability of devices and an enhancement in digital literacy skills.
The region is poised to witness over 3 billion smartphone connections by 2030, corresponding to a smartphone adoption rate of 94 percent, surpassing the global average of 92 percent. This surge in smartphone connections is evident across both mature and emerging markets in the region.
In terms of mobile data traffic, the region is projected to witness more than a twofold increase by 2030. The burgeoning growth of mobile data traffic is intrinsically linked to the proliferation of 5G technology, as indicated by 5G’s increasing share of overall mobile data traffic. Notably, 5G subscribers demonstrate more interest in expanding their mobile contracts to include additional services and content, as per a GSMA Intelligence survey.
Video streaming and online gaming rank among the top services and content utilized by 5G users in Asia Pacific. For instance, Telkomsel’s Dunia Games, a leading esports organizer in Indonesia, hosts the Dunia Games WIB Championship, a renowned event attended by over 45 professional teams and attracting more than 14 million online viewers.
As Asia Pacific embraces the transformative potential of 5G technology, the landscape of mobile connectivity is poised for a paradigm shift, with widespread implications across industries and communities.
