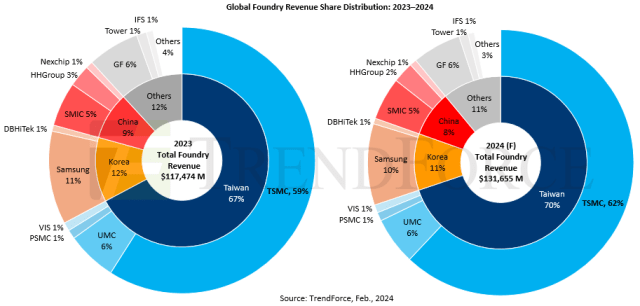
In a recent report by TrendForce, the global foundry revenues for the year 2023 have skyrocketed to $117.47 billion, with Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) solidifying its dominance by capturing 60 percent share.
TSMC’s strategies in key global locations have played a pivotal role in its unprecedented success. TSMC has strategically identified the United States, Japan, and Germany as crucial hubs for its advanced and mature factories. Among these, Japan has emerged as a frontrunner, with projects progressing at an accelerated pace, some even surpassing initial timelines.
The inauguration of TSMC’s Kumamoto Plant (JASM) in Japan on the 24th February signifies a leap into the future for the semiconductor giant.
This marks TSMC’s first factory in Japan, dubbed Fab-23, heralding a era of technological advancement. TrendForce anticipates the plant’s total capacity to range between a robust 40,000 to 50,000 wafers per month (wpm), with a primary focus on 22/28nm processes complemented by 12/16nm technologies, setting the stage for further expansion in Kumamoto.
Japan’s Semiconductor Landscape Transformed as TSMC Leads the Charge
Japan’s ascendancy in the semiconductor industry’s upstream sectors, bolstered by stalwarts such as TEL, JSR, SCREEN, SUMCO, and Shin-Etsu, has positioned the nation uniquely for future endeavors.
TrendForce envisions the emergence of three semiconductor powerhouses in Kyushu, Tohoku, and Hokkaido, with Kyushu spearheading the charge, notably as the home of TSMC’s Kumamoto plant.
Hokkaido’s Rapidus, with its ambitious pursuit of the 2nm process, aims to stimulate economic growth, underscoring Japan’s concerted efforts across industry, government, and academia to foster a comprehensive semiconductor manufacturing ecosystem.
The concentration of semiconductor enterprises in Kyushu and Tohoku regions, coupled with Tohoku University’s expertise in semiconductor development, underscores Japan’s burgeoning prominence in the global arena. Major players like ROHM, Renesas, and PSMC are making substantial investments, exemplified by PSMC’s establishment of a new 12-inch wafer fab in Sendai.
Kyushu’s abundance of underground water resources, vital for semiconductor production, has attracted industry giants such as SUMCO, TOK, Sony, ROHM, and Mitsubishi Electric, cementing its status as an ideal location for semiconductor manufacturing. TSMC’s decision to expand in Kyushu was primarily influenced by the region’s water resources.
As the competition heats up for the location of TSMC’s third plant, contenders like Fukuoka in Kyushu and potentially Osaka in the Kansai region have emerged. While still in the nascent planning stages, possibilities abound for the future trajectory of the project.
Initially focused on 6/7nm processes, advancements may propel the third plant to embrace cutting-edge technologies like 5nm or 3nm processes, underscoring TSMC’s relentless pursuit of innovation.
Moreover, TSMC’s establishment of a 3DIC research center in Ibaraki and plans for an advanced packaging plant in Japan underscore its commitment to a comprehensive presence, solidifying Japan’s standing in the semiconductor landscape from front-end manufacturing to back-end packaging and testing.
